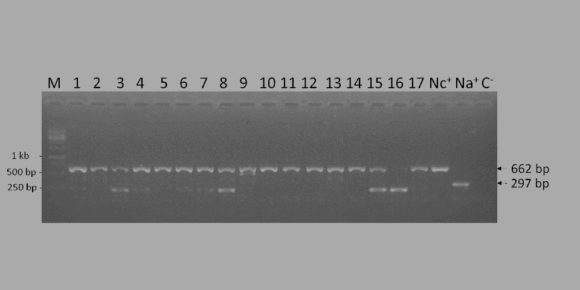
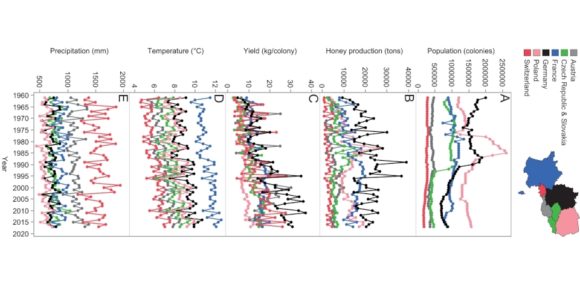
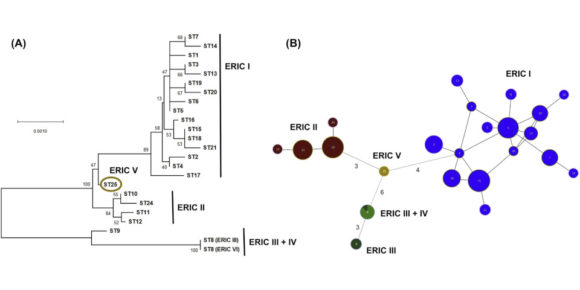
Changes in chemical cues of Melissococcus plutonius infected honey bee larvae
Abstract European foulbrood (EFB), caused by Melissococcus plutonius, is a globally distributed bacterial brood disease affecting Apis mellifera larvae. There is some evidence, even if under debate, that spreading of the disease within the colony is prevented by worker bees performing hygienic behaviour, including detection and removal of infected larvae. Olfactory cues (brood pheromones, signature…