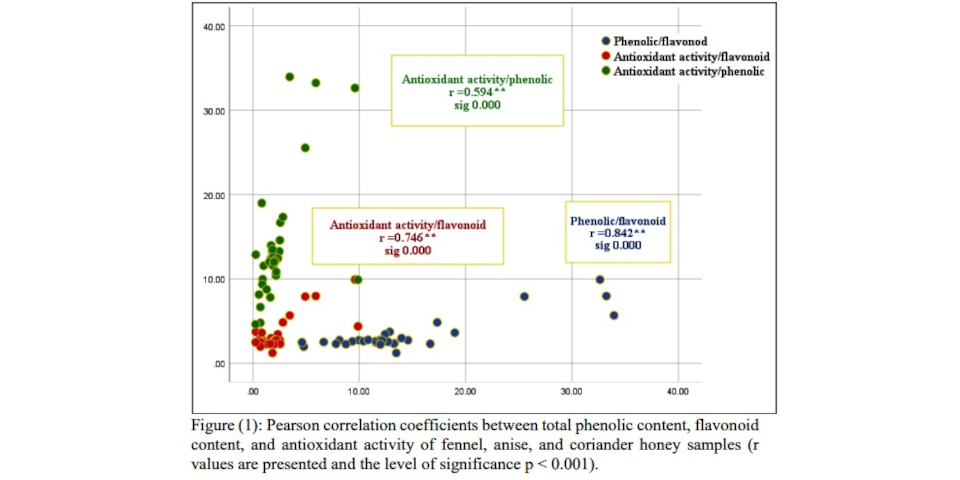
Honey is regarded as a functional food that has health-promoting qualities. However, the specific composition of each type of honey can impact its potential health advantages. The aim of this study was to evaluate the characterization and differentiation of physicochemical, biological, and melissopalynology analysis of three types of honey (fennel, anise, and coriander honey), from upper Egypt. The physicochemical properties (E.C, specific gravity, T.S.S, moisture , pH, free acidity, lactone, total acidity, (HMF), and total protein ) were determined. In addition, total flavonoid content, total phenolic content, antibacterial , and antioxidant activity, and melissopalynology analysis were also evaluated in the samples. The physicochemical parameters of honey types are generally similar. As such, it isn’t easy to differentiate between three types of honey based on the physicochemical analysis. Still, there’s a significant difference in phenolic content between coriander honey and fennel or anise honey. In comparison, no significant differences were recorded in total flavonoid content or antioxidant activity among the three types of honey and flavonoid showed a highly significant positive correlation with antioxidant activity, in addition, the data of antibacterial were generally similar in the three types of honey under study, melissopalynology analysis showed that there’s a slight difference in the shape of fennel, anise, coriander pollen grain. The difficulty of differentiating these honey types may be due to the very similarity in plant chemical composition, which belongs to the same plant family (Apiaceae). This study will help the researcher and honey producer identify pure honey and verify its authenticity.
2417 Members
127 Countries!
127 Countries!