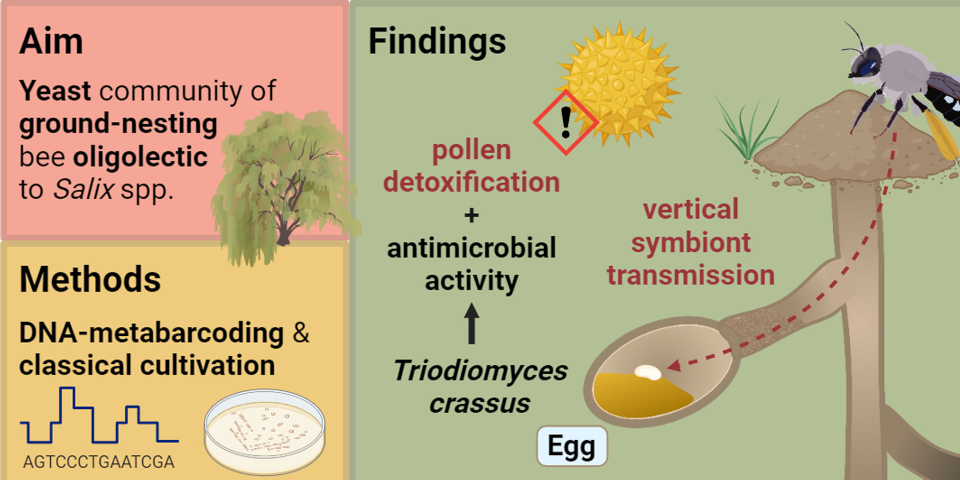
To fully understand a species, it is essential to gain knowledge about their associated (micro-)organisms. Currently, most research focuses on managed social bees and their bacterial associates. Functional descriptions of bee-fungi-interactions in solitary bee species, particularly in ground-nesting bees, are lacking. In this study, we identified the yeast community composition associated with the oligolectic mining bee Andrena vaga. We analysed seven different matrices of the early nest stage, using both classical cultivation and ITS2 DNA-metabarcoding. Our results support recent findings that solitary bees can exhibit core microbiomes and give first indications of vertical symbiont transmission for solitary bees, previously only observed in social bees. Particularly, the eggs showed a very distinct yeast composition, with the dimorphic yeast Triodiomyces crassus being the only cultivated species from all egg samples. This smut-related species assimilates salicin and produces antimicrobial glycolipids, potentially used for pollen detoxification and brood cell disinfection. Hence, yeast associates might be a key factor enabling oligolectic bees to specialise on toxic pollen sources. Other identified yeasts, such as Starmerella bombicola, are discussed in terms of their ecology and functionality. Our study provides insights into the crucial role of associated microorganisms and might be the missing link to understand the origin of oligolecty.
2424 Members
127 Countries!
127 Countries!