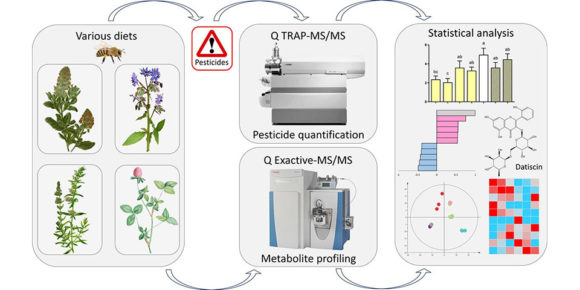
Metabolomics unveils the influence of dietary phytochemicals on residual pesticide concentrations in honey bees
The losses of honey bee colonies and declines of other insect pollinators have been associated with negative effects of pesticides. Honey bees as well as other pollinators are nectar and pollen foragers and thus are exposed to an extensive range of phytochemicals. Understanding the synergistic, additive, and antagonistic effects of plant secondary metabolites and pesticides…