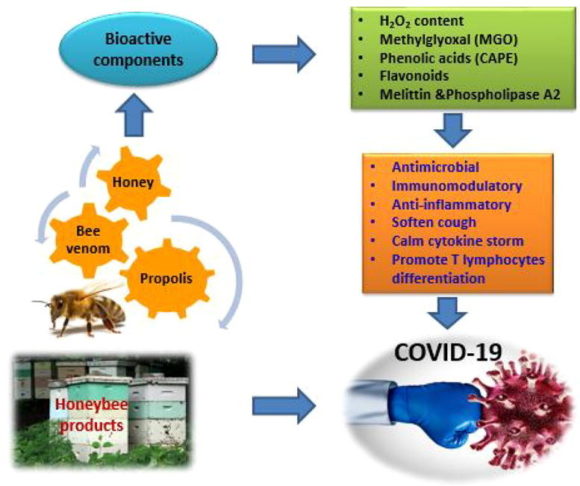
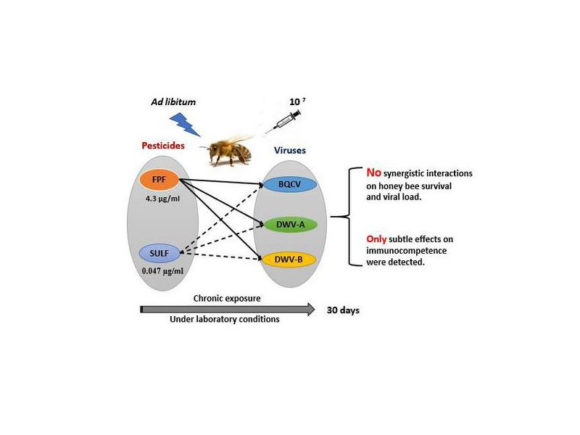
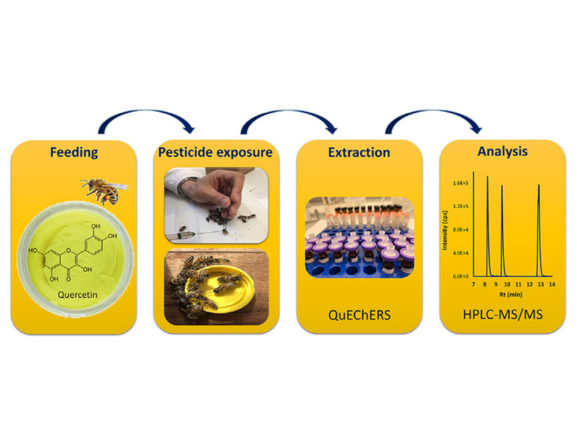
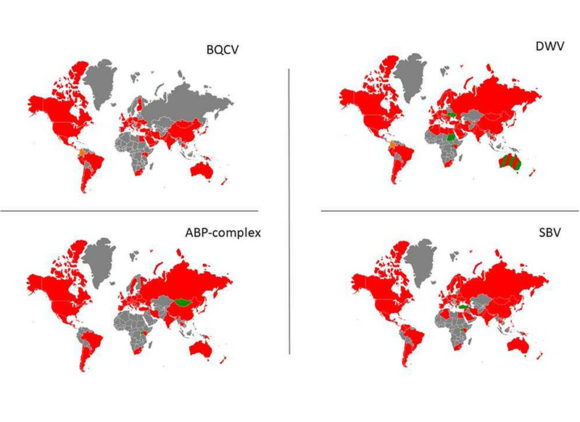
LC–MS/MS Quantification Reveals Ample Gut Uptake and Metabolization of Dietary Phytochemicals in Honey Bees
Nanna Hjort Vidkjær, Inge S. Fomsgaard, and Per Kryger Abstract: The honey bee pollen/nectar diet is rich in bioactive phytochemicals and recent studies have demonstrated the potential of phytochemicals to influence honey bee disease resistance. To unravel the role of dietary phytochemicals in honey bee health it is essential to understand phytochemical uptake, bioavailability, and metabolism but presently…